The main reason outdoor water can carry dangerous diseases is the interaction between the natural environment and human activities. In nature, water can serve as a medium for the transmission of bacteria, viruses, parasites, and chemicals.In daily life, rainwater seems to be a refreshing and nourishing gift from nature. However, we may not have considered that rainwater may actually harbor various bacteria and viruses, posing certain risks to our health and lives.Outdoor water may carry dangerous diseases, mainly because it is susceptible to various pathogens and pollutants, which can be transmitted to humans through multiple pathways.
Potentially Transmitted Diseases and Their Causes

- Skin-to-Skin Contact Diseases
- Fungal Infections (such as tinea pedis): Humid environments foster fungal growth, and contact with the poolside or locker room floor can lead to infection.
- Bacterial Infections: Unsafe water can cause folliculitis, impetigo, and other skin conditions, manifesting as redness, itching, or ulcers.
- Mucous Membrane Contact Diseases
- Pink Eye (Conjunctivitis): Bacteria or viruses in pool water can enter the eyes and cause infection, resulting in redness, swelling, and increased discharge.
- Urinary Tract Infections: Women are more susceptible to urinary tract infections due to contaminated water due to their anatomy.
- Digestive Tract Diseases
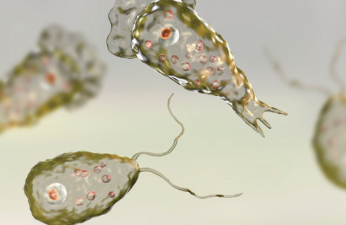
- Parasitic Infections (such as Cryptosporidium): Swallowing contaminated water can cause diarrhea and abdominal pain, with children being particularly at risk. - Bacillary dysentery or cholera: Natural waters contaminated with fecal matter can spread serious intestinal infections.

High-risk scenarios and protective measures
- Public swimming pool hazards
- Incomplete disinfection: Inadequate chlorine concentration or untimely water changes may leave pathogens.
- Crowded areas: Sharing facilities (such as handrails and lounge chairs) can increase the risk of cross-infection.
- Protective measures: Choose a pool with a high hygiene rating and shower and wipe down immediately after swimming.
- Natural water risks
- Pollution threat: Upstream sewage, animal feces, algal toxins, and other sources can contaminate lakes and rivers.
- Protective measures: Avoid swimming in water with dead fish, foul odors, or turbidity, and avoid swallowing river water.
- Personal protection tips
- Wound protection: Avoid entering the water if your skin is broken, or cover it with a waterproof dressing.
- Goggles and a swim cap: Reduce contact with dirty water and prevent contaminants from being carried by your hair.
- Bring cleaning supplies: Use your own towel and avoid sharing personal items.
Misconceptions Debunked
"Residual chlorine in swimming pools = absolutely safe": Residual chlorine can only kill some microorganisms, not all pathogens.
"Clear = clean": Water clarity is not directly correlated with microbial contamination and should be considered in conjunction with disinfection records.
By choosing a reputable venue, practicing personal protection, and cleaning your body promptly, you can effectively enjoy the fun of swimming while minimizing health risks. If you experience symptoms such as fever, rash, or diarrhea after a swim, it is recommended that you seek medical attention promptly and disclose your history of water exposure.